TECHNOLOGY
Twitter risks fraying as engineers exit over Musk upheaval
Published
1 year agoon
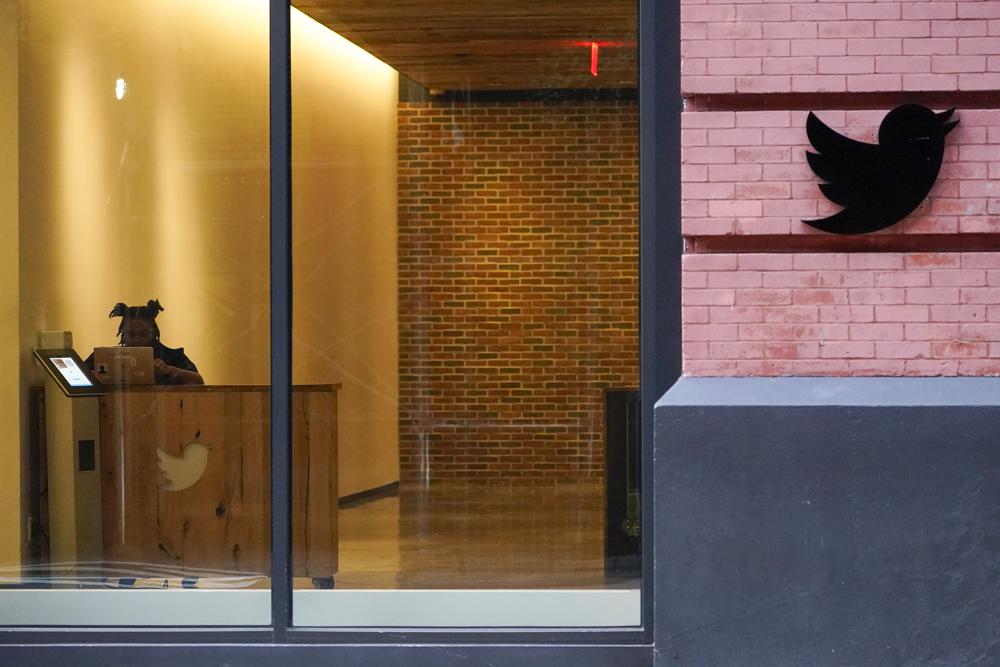

Elon Musk’s managerial bomb-throwing at Twitter has so thinned the ranks of software engineers who keep the world’s de-facto public square up and running that industry insiders and programmers who were fired or resigned this week agree: Twitter may soon fray so badly it could actually crash.
Musk ended a very public argument with nearly two dozen coders over his retooling of the microblogging platform earlier this week by ordering them fired. Hundreds of engineers and other workers then quit after he demanded they pledge to “extremely hardcore” work by Thursday evening or resign with severance pay.
The newest departures mean the platform is losing workers just at it gears up for the 2022 FIFA World Cup, which opens Sunday. It’s one of Twitter’s busiest events, when tweet surges heavily stress its systems.
“It does look like he’s going to blow up Twitter,” said Robert Graham, a veteran cybersecurity entrepreneur. “I can’t see how the lights won’t go out at any moment” — although many recently departed Twitter employees predicted a more gradual demise.
Hundreds of employees signaled they were leaving ahead of Thursday’s deadline, posting farewell messages, a salute emoji or other familiar symbols on the company’s internal Slack messaging board, according to employees who still have access. Dozens also took publicly to Twitter to announce their departure.
Earlier in the week, some got so angry at Musk’s perceived recklessness that they took to Twitter to insult the Tesla and Space X CEO. “Kiss my ass, Elon,” one engineer said, adding lipstick marks. She had been fired.
Twitter leadership sent an unsigned email after Thursday’s deadline saying its offices would be closed and employee badge access disabled until Monday. No reason was given, according to two employees who got the email— one who took the severance, one still on payroll. They spoke on condition of anonymity, fearing retribution.
A trusted phalanx of Tesla coders at his side as he ransacked a formerly convivial workspace, Musk didn’t appear bothered.
“The best people are staying, so I’m not super worried,” he tweeted Thursday night. But it soon became clear some crucial programming teams had been thoroughly gutted.
Indicating how strapped he is for programmers, Musk sent all-hands emails Friday summoning “anyone who actually writes software” to his command perch on Twitter’s 10th floor at 2 p.m. — asking that they fly into San Francisco if not local, said the employee who quit Thursday but was still receiving company emails.
After taking over Twitter less than three weeks ago, Musk booted half of the company’s full-time staff of 7,500 and an untold number of contractors responsible for content moderation and other crucial efforts. Then came this week’s ultimatum.
Three engineers who left this week described for The Associated Press why they expect considerable unpleasantness for Twitter’s more than 230 million users now that well over two-thirds of Twitter’s pre-Musk core services engineers are apparently gone. While they don’t anticipate near-term collapse, Twitter could get very rough at the edges — especially if Musk makes major changes without much off-platform testing.
Signs of fraying were evident before Thursday’s mass exit. People reported seeing more spam and scams on their feeds and in their direct messages. Engineers reported dropped tweets. People got strange error messages.
Still, nothing critical has broken. Yet.
“There’s a betting pool for when that happens,” said one of the engineers, all of whom spoke on condition of anonymity for fear of retaliation from Musk that could impact their careers and finances.
Another said that if Twitter has been shutting servers and “high volume suddenly comes in, it might start crashing.”
“World Cup is the biggest event for Twitter. That’s the first thing you learn when you onboard at Twitter,” he said.
With the earlier layoffs of curation employees, Twitter’s trending pages were already suffering. The engineering fireworks began Tuesday when Musk announced on Twitter that he had begun shutting down “microservices” he considered unnecessary “bloatware.”
“Less than 20% are actually needed for Twitter to work!” he tweeted.
That drew objections from engineers who told Musk he had no idea what he was talking about.
“Microservices are how most modern large web services organize their code to allow software engineers to work quickly and efficiently,” said Gergely Orosz, author of the Pragmatic Engineer blog and a former Uber programmer. There are scores of such services and each manages a different feature. Instead of testing the removal of microservices in a simulated real-world environment, Musk’s team has apparently been updating Twitter live on everyone’s computers.
And indeed, one microservice briefly broke — the one people use to verify their identity to Twitter via SMS message when they log in. It’s called two-factor authentication.
“You have hit the limit for SMS codes. Try again in 24 hours,” Twitter advised when a reporter tried to download their microblogging history archive. Luckily, the email verification alternative worked.
One of the newly separated Twitter engineers, who had worked in core services, told the AP that engineering team clusters were down from about 15 people pre-Musk — not including team leaders, who were all laid off — to three or four before Thursday’s resignations.
Then more institutional knowledge that can’t be replaced overnight walked out the door.
“Everything could break,” the programmer said.
It takes six months to train someone to work an on-call rotation for some services, the engineers said. Such rotations require programmers to be available at all hours. But if the person on call is unfamiliar with the code base, failures could cascade as they frantically plow through reference manuals.
“If I stayed I would have been on-call constantly with little support for an indeterminate amount of time on several additional complex systems I had no experience in,” tweeted Peter Clowes, an engineer who took the severance.
“Running even relatively boring systems takes people who know where to go when something breaks,” said Blaine Cook, Twitter’s founding engineer, who left in 2008. It’s dangerous to drastically reduce a programming workforce to a skeleton crew without first bulletproofing the code, he said.
“It’s like saying, ‘These firefighters aren’t doing anything. So, we’ll just fire them all.’”
The engineers also worry Musk will shut down tools involved in content moderation and removing illicit material that people upload to Twitter — or that there simply wouldn’t be enough people on staff to run them properly.
Another concern is hackers. When they’ve breached the system in the past, diminishing damage depends on detecting them quickly and kicking them out.
It’s not clear how Musk’s housecleaning at Twitter has affected its cybersecurity team, which suffered a major PR black eye in August when the highly respected security chief fired by the company earlier this year, Peiter Zatko, filed a whistleblower complaint claiming the platform was a cybersecurity shambles.
“So much of the security infrastructure of a large organization like Twitter is in people’s heads,” said Graham, the cybersecurity veteran. “And when they’re gone, you know, it all goes with them.”
TECHNOLOGY
How much YouTube pays for 1 million views, according to creators
Published
12 months agoon
May 6, 2023
- YouTube creators earn money from Google-placed ads on their videos.
- A number of factors determine how much money they make, including video views.
- Creators said how much YouTube pays for 1 million views ranged from $3,400 to $30,000.
While many factors — content niche and country, among them — determine how much money a YouTuber earns on any particular video, the number of views it gets is perhaps the most significant.
When a YouTube video hits 1 million views, there’s almost a guaranteed big payday for its creator. In some cases, creators can make five-figures from a single video if it accrues that many views.
Three creators explained how much money YouTube had paid them. YouTube pays $3,400 to $30,000 for 1 million views, these creators said.
When tech creator Shelby Church spoke with Insider, she had earned $30,000 from a video about Amazon FBA (Fulfillment By Amazon). At the time, the video had accrued 1.8 million views.
Her RPM rate — or earnings per 1,000 views — are relatively high, she said, because of her content niche. Business, personal finance, and technology channels tend to earn more per view.
“YouTubers don’t always make a ton of money, and it really depends on what kind of videos you’re making,” she said.
Influencers can earn 55% of a video’s ad revenue if they are part of YouTube’s Partner Program, or YPP. To qualify for the program, they must have 1,000 subscribers and 4,000 hours of watch time on their long-form videos.
They can also make money from shorts, YouTube’s short-form video offering. In order to qualify, creators need to reach 10 million views in 90 days and have 1,000 subscribers. YouTube pools ad revenue from shorts and pays an undisclosed amount to record labels for music licensing. Creators receive 45% of the remaining money based on their percentage of the total shorts views on the platform.
You can share this story on social media:
PLEASANT MUSIC FOR YOUR CAFE, BAR, RESTAURANT, SWEET SHOP, HOME
SUITABLE MUSIC FOR YOGA LOVERS
TECHNOLOGY
Tesla employees shared sensitive images recorded by cars – Reuters
Published
1 year agoon
April 8, 2023
Some pictures were turned into memes and distributed through internal chats, former workers told the agency
Tesla workers shared “highly invasive” images and videos recorded by customers’ electric cars, making fun of them on internal chat groups, several former employees of Elon Musk’s company have told Reuters.
The electric-car manufacturer obtains consent from its clients to collect data from vehicles in order to improve its self-driving technology. However, the company assures owners that the whole system is “designed from the ground up to protect your privacy,” the agency pointed out in its report on Thursday.
According to nine former workers who talked to the agency, groups of employees shared private footage of customers in Tesla’s internal one-on-one chats between 2019 and 2022.
One of the clips in question captured a man approaching his electric car while he was completely naked, one of the sources said.
Tesla recalls over 360,000 cars over self-driving threat
Others featured crashes and road-rage incidents. One particular video of a Tesla hitting a child on a bike in a residential area spread around the company’s office in San Mateo, California “like wildfire,” an ex-employee claimed.
“I’m bothered by it because the people who buy the car, I don’t think they know that their privacy is, like, not respected… We could see them doing laundry and really intimate things. We could see their kids,” another former worker told the agency.
Seven former employees also told Reuters that the software they used at work allowed them to see the location where the photo or video was made, despite Tesla assuring its customers that “camera recordings remain anonymous and are not linked to you or your vehicle.”
The agency noted that it could not obtain any of the pictures or clips described by its sources, who said they were all deleted. Some former employees also told the journalists that they had only seen private data being shared for legitimate purposes, such as seeking assistance for colleagues. Tesla did not respond when approached for comment on the issue by Reuters.
You can share this story on social media!
PLEASANT MUSIC FOR YOUR CAFE, BAR, RESTAURANT, SWEET SHOP, HOME
SUITABLE MUSIC FOR YOGA LOVERS
TECHNOLOGY
Nordic nation’s military bans use of TikTok – media
Published
1 year agoon
March 27, 2023
Sweden’s Defense Ministry has reportedly barred employees from using the Chinese-owned app on their work phones
Sweden’s military has reportedly cracked down on TikTok, decreeing that staff members are no longer allowed to use the Chinese-owned video-sharing application on their devices at work because of security concerns.
The Swedish Defense Ministry on Monday issued its decision, which was viewed by Agence-France Presse, banning the use of TikTok. Security concerns were raised based on “the reporting that has emerged through open sources regarding how the app handles user information and the actions of the owner company, ByteDance,” the ministry said.
The move follows similar restrictions imposed by other EU countries in recent weeks. For example, France banned government employees from downloading “recreational applications,” including TikTok, on their work phones. Norway barred use of the app on devices that can access its parliament’s computer network, while the UK and Belgium banned it on all government phones. Denmark’s Defense Ministry and Latvia’s Foreign Ministry imposed their TikTok bans earlier this month.
China responds to TikTok allegations
“Using mobile phones and tablets can in itself be a security risk, so therefore we don’t want TikTok on our work equipment,” Swedish Defense Ministry press secretary Guna Graufeldt told AFP.
The US, Canada and New Zealand previously banned their federal employees from using TikTok on government-issued devices, citing fears of ByteDance’s ties to the Chinese Communist Party (CCP). Members of Congress may try to ban the app from the US market altogether after testimony at a congressional hearing last week by TikTok CEO Shou Zi Chew failed to ease their security concerns. “They’ve actually united Republicans and Democrats out of the concern of allowing the CCP to control the most dominant media platform in America,” US Representative Mike Gallagher said on Sunday in an ABC News interview.
Chinese officials have denied claims that TikTok is used to collect the personal data of its American users. “The Chinese government has never asked and will never ask any company or individual to collect or provide data, information or intelligence located abroad against local laws,” Chinese Foreign Ministry spokeswoman Mao Ning told reporters last week. She added that Washington has attacked TikTok without providing any evidence that it threatens US security.
PLEASANT MUSIC FOR YOUR CAFE, BAR, RESTAURANT, SWEET SHOP, HOME
SUITABLE MUSIC FOR YOGA LOVERS



Global debt balloons to record highs

German military to sell tons of toilet paper

First female Saudi astronaut heads to space

Nigeria takes step to combat fuel shortages

US will default if debt deal fails – treasury secretary

Village People demand Trump stop using their music

Hollywood star pulls out of hosting awards show amid strike

Rock icon slams German authorities

Agatha Christie novels chopped by ‘sensitivity readers’ – media

Marvel star back in training after breaking over 30 bones
Turkish minister escapes fire blast (VIDEO)

Trump savages pop star’s Super Bowl performance

Alec Baldwin sued by Ukrainian family of slain cinematographer

Duran Duran stumbles, Dolly Parton rolls into Rock Hall

Sweden probes possible plot behind Russian pipeline leaks

FINANCE


Global debt balloons to record highs
It’s now $45 trillion higher than its pre-pandemic level and is expected to continue growing rapidly, a top trade body...


Nigeria takes step to combat fuel shortages
The West African country has built a giant oil refinery to cover domestic demand Nigeria will commission its new Dangote...


US will default if debt deal fails – treasury secretary
The current borrowing limit is a constraint on Washington’s ability to meet its obligations, Janet Yellen insists America’s chances of...


Facebook parent Meta fined €1.2 billion by Irish watchdog
The American tech company has been accused of violating EU data privacy rules US tech giant Meta has been hit...


UK’s business with sanctioned country booming
Trade between Britain and Iran has reached the highest level in a decade, according to official data, apparently having been...

POLITICS


Erdogan election defeat would be ‘revenge’ – Syrian Kurds
The YPG claims the Turkish president failing to win another term would be payback for Ankara’s counter-terrorism operations in Syria...


Chinese special envoy meets with Zelensky
Li Hui visited Kiev to share Beijing’s views on a political settlement to the Ukraine crisis Ukrainian President Vladimir Zelensky...


Pakistan’s top court orders release of former PM Imran Khan
Pakistan’s Supreme Court has ordered the release of former prime minister Imran Khan, whose arrest earlier this week triggered deadly...


Kamala Harris to run AI taskforce
The US vice president will ask AI execs to evaluate the safety and fairness of their models US Vice President...


Most Americans want to move on from Biden and Trump – poll
70% of respondents said the incumbent shouldn’t bid for office in 2024, with that figure 60% for the Republican former...

OPINION


Disgraced ex-PM Liz Truss seeks to ruin any hopes for normal UK-China ties
The former premier’s Taiwan trip is nothing but a provocation for Beijing to lash out at London, sinking any constructive...


India facing challenge to steer SCO agenda away from Western-dominated frameworks
The Shanghai Cooperation Organisation is looking at ways to address the most pressing global issues without being a disruptive influence...


China isn’t the biggest threat to Italy’s prosperity
Rome is considering leaving the Belt and Road Initiative in a move which will place virtue signaling to other Western...


Meet the Czech lawyer who rallies thousands to shake up the EU establishment
In mid-April, a fledgling political party that recently formed in the Czech Republic called Pravo Respekt Odbornost (Law Respect Expertise;...


UK shows signs of good will to China, but it’s not the one calling the shots in this relationship
The British foreign secretary says antagonizing Beijing goes against London’s ‘national interests’, but Washington has other ideas British Foreign Secretary...

LIFE


conic Smiths bassist dies aged 59
The bassist with legendary English rock band The Smiths, Andy Rourke, has died at the age of 59, the group’s...


Village People demand Trump stop using their music
A viral video emerged last week of Donald Trump dancing to a Village People song at his Florida estate Village...


Hollywood star pulls out of hosting awards show amid strike
Drew Barrymore is stepping down as host of this year’s MTV Movie & Music Awards, due to be held on...


Mexico condemns US ‘interference’ in drug war
The DEA’s infiltration of the Sinaloa Cartel without state permission amounts to espionage, the Mexican president says Mexican President Andres...


Rock icon slams German authorities
Pink Floyd co-founder Roger Waters criticized the city of Frankfurt for canceling his concert and vowed to take legal action...



Trending
-

 TECHNOLOGY12 months ago
TECHNOLOGY12 months agoHow much YouTube pays for 1 million views, according to creators
-

 FINANCE11 months ago
FINANCE11 months agoFacebook parent Meta fined €1.2 billion by Irish watchdog
-

 LIFE12 months ago
LIFE12 months agoHollywood star pulls out of hosting awards show amid strike
-

 LIFE11 months ago
LIFE11 months agoconic Smiths bassist dies aged 59
-

 NEWS11 months ago
NEWS11 months agoKenya supports creation of pan-African court
-

 FINANCE11 months ago
FINANCE11 months agoUS will default if debt deal fails – treasury secretary
-

 FINANCE11 months ago
FINANCE11 months agoGlobal debt balloons to record highs
-

 WAR11 months ago
WAR11 months agoUkraine won’t join NATO anytime soon – Scholz